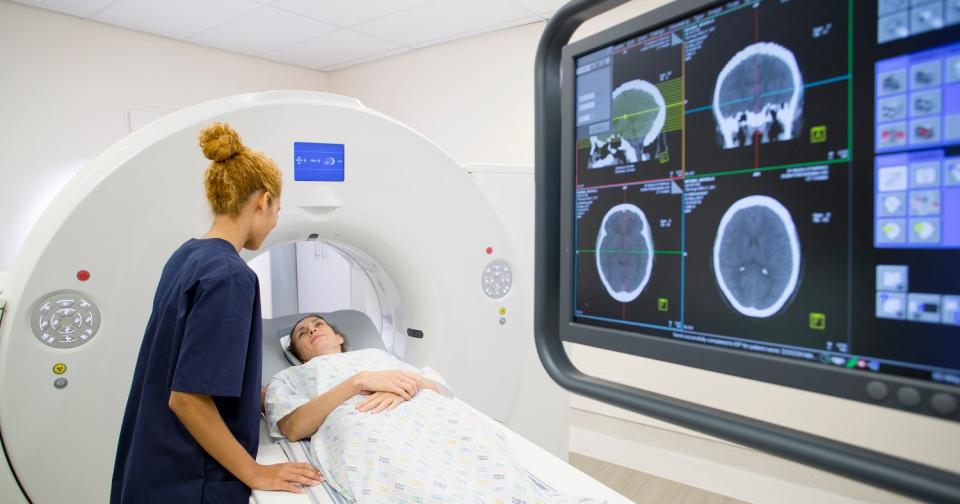
In the fast-paced world of healthcare, a ct tech plays a crucial role in diagnostic imaging. Also known as a computed tomography technologist, this professional operates advanced CT scanners to produce detailed cross-sectional images of patients’ bodies. These images help physicians detect diseases, injuries, and abnormalities with precision. If you’re considering a career in medical imaging, understanding the responsibilities and path to becoming a ct tech is essential.
What Is a CT Tech?
A ct tech specializes in computed tomography, a non-invasive imaging technique that uses X-rays and computer processing to create 3D visuals of internal structures. Unlike traditional X-rays, CT scans provide layered views, making them invaluable for diagnosing conditions like tumors, fractures, and internal bleeding.
Key Responsibilities of a CT Tech
Ct techs prepare patients for scans by explaining procedures and ensuring comfort. They position individuals correctly on the scanning table. Equipment is operated by them to capture high-quality images while minimizing radiation exposure. After the scan, images are reviewed for clarity before sending them to radiologists. Patient safety remains a top priority, with ct techs following strict protocols to shield non-targeted areas from radiation.
Ct techs often collaborate with healthcare teams. They adjust scan parameters based on patient needs, such as slice thickness or contrast use. In emergencies, quick thinking is required to handle trauma cases efficiently.
The Technology Behind CT Scans
Computed tomography has evolved significantly since its introduction in the 1970s. Modern CT scanners rotate around the body, capturing multiple X-ray beams that a computer reconstructs into detailed images. This process allows for rapid scans, often completed in minutes.
Differences Between CT, MRI, and X-Ray
CT scans excel in imaging bones and detecting acute issues like strokes, where speed matters. MRIs, using magnetic fields, are better for soft tissues without radiation but take longer. X-rays provide quick, basic views but lack the depth of CT. A ct tech must understand these distinctions to recommend the right modality when consulting with physicians.
Advancements like PET/CT combine metabolic data with anatomical details, aiding cancer detection. SPECT/CT offers similar benefits for cardiac and neurological assessments.
How to Become a CT Tech
Pursuing a career as a ct tech requires structured education and certification. Most start with foundational training in radiology before specializing.
Educational Requirements
An associate’s degree in radiologic technology is the typical entry point. Programs last about two years and cover anatomy, physiology, patient care, and radiation physics. Coursework includes hands-on lab sessions where students practice imaging techniques.
Some opt for a bachelor’s degree for advanced roles. Accredited programs by the Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology ensure quality. Online options exist for working professionals seeking flexibility.
Certification and Licensure
Certification is obtained through the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT). To qualify for the CT post-primary exam, one must hold primary certification in radiography, nuclear medicine, or radiation therapy. The exam tests knowledge in patient care, safety, image production, and procedures.
Clinical experience is mandated—ARRT requires 125 procedures across categories like head, spine, and musculoskeletal scans. State licensure varies; about 75% of states require it, often aligning with ARRT standards. Continuing education, or CE credits, must be completed every two years to maintain credentials.
Skills Needed for Success
Technical proficiency is key, but interpersonal skills matter too. Ct techs communicate effectively to ease patient anxiety. Attention to detail prevents errors in imaging. Physical stamina helps with long shifts and patient positioning. Problem-solving aids in troubleshooting equipment issues.
CT Tech Career Outlook and Salary
The demand for ct techs is growing due to an aging population and increased reliance on diagnostic imaging. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 4% job growth from 2024 to 2034, faster than average.
Salary Expectations
Median annual salary for radiologic technologists, including ct techs, stands at $78,980 as of 2024. Travel ct techs earn more, with weekly pay ranging from $2,240 to $4,200 depending on location and experience. Factors like certifications, shift work, and urban settings boost earnings. Entry-level positions start around $60,000, while experienced specialists can exceed $90,000.
Job Settings and Advancement
Most ct techs work in hospitals, but opportunities exist in outpatient clinics, imaging centers, and physician offices. Shifts may include evenings or weekends for emergency coverage.
Career growth includes roles like lead ct tech, imaging supervisor, or educator. Some advance into management or specialize in areas like cardiac CT. Networking at conferences and pursuing advanced certifications open doors.
Challenges and Rewards in the Field
Working as a ct tech involves exposure to radiation, managed through protective gear and monitoring. High-pressure environments demand resilience, especially in trauma units.
Rewards include making a direct impact on patient outcomes. Accurate scans lead to timely treatments, saving lives. The field offers variety, with each day bringing new cases. Job satisfaction comes from combining technology with compassionate care.
Technology changes rapidly, requiring ongoing learning. Innovations like AI-assisted imaging promise to enhance efficiency, reducing scan times and improving accuracy.
FAQs
What is the difference between a CT tech and a radiologic technologist?
A ct tech is a specialized radiologic technologist focused on computed tomography scans. General radiologic techs handle various imaging like X-rays, while ct techs deal with advanced cross-sectional imaging.
How long does it take to become a CT tech?
It typically takes 2-4 years: 2 years for an associate’s degree in radiology, plus time for ARRT certification and clinical experience in CT.
Do CT techs need to be licensed in every state?
No, but most states require licensure. Check local regulations, as they often align with ARRT certification.
What are the salary prospects for travel CT techs?
Travel ct techs can earn $2,240-$4,200 weekly, including benefits like housing and travel reimbursements, depending on assignment location.
Is there high demand for CT techs?
Yes, demand is rising due to aging populations and advancements in medical imaging, with steady job growth projected.